GitLab¶
1. Plan¶
Issues¶
With the GitLab Issue Tracker you can develop ideas together how you can solve problems and plan work. The issues are always linked to a specific project, but they can also be displayed to all members of a group. They are mostly used to
discuss the implementation of new ideas
track the progress of the tasks
include suggestions and (support) questions
develop implementations
You can refer to issues and have this link displayed. Similar issues can also be marked. Alternatively, you can also use external issue trackers like Jira.
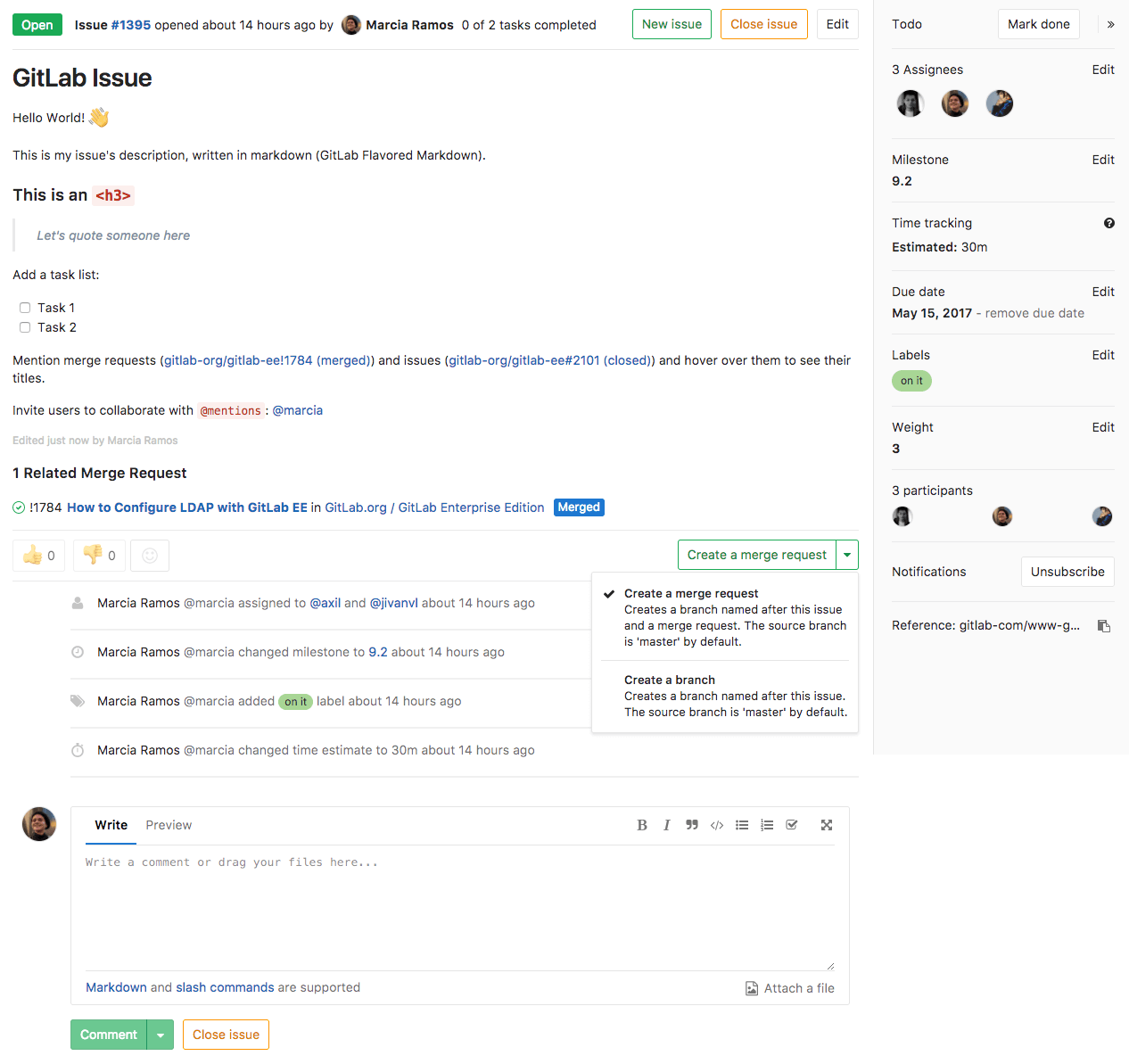
Issue page¶
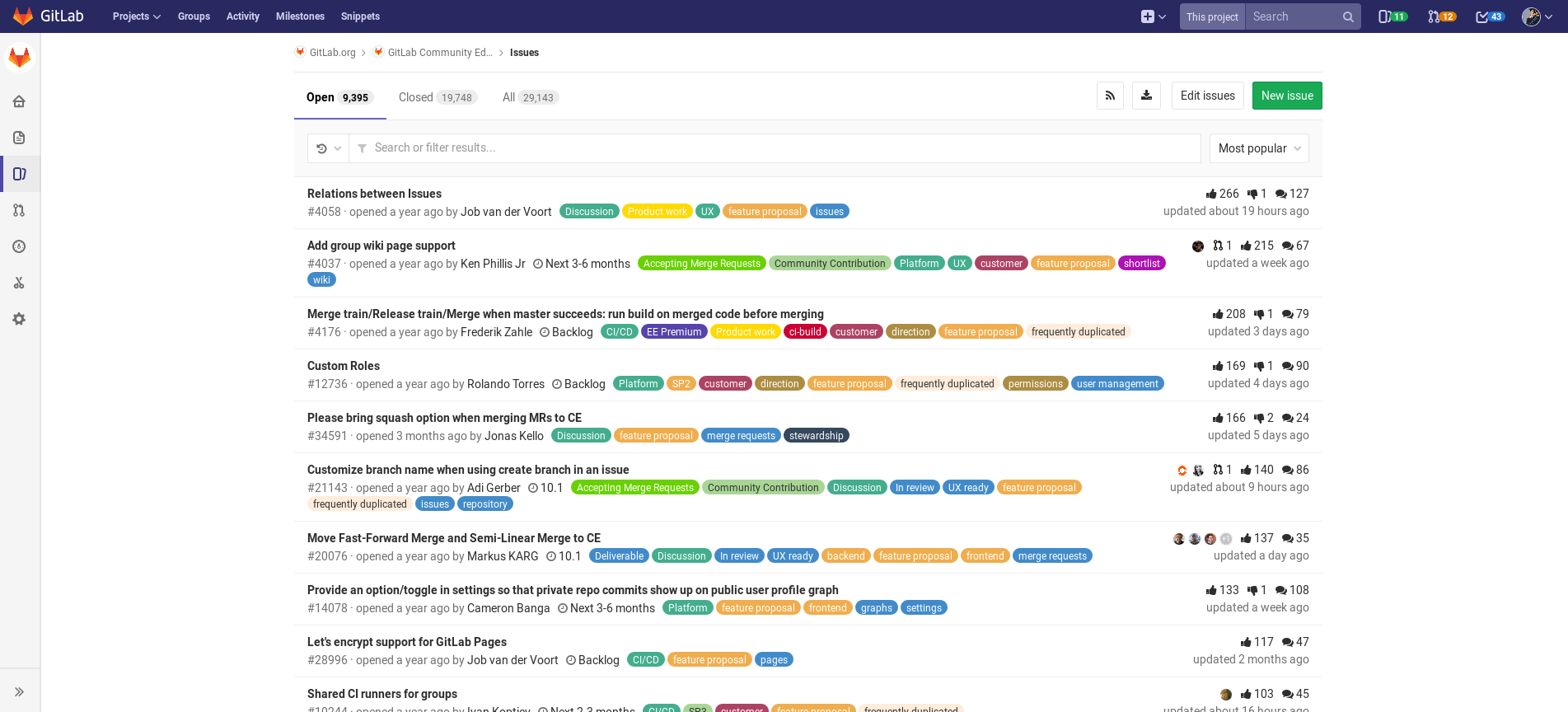
Issue list¶
Kanban Boards¶
You can use Kanban boards to plan, organise and visualise workflows. With them you can quickly track issues and manage projects.
In addition to Kanban boards, you can also display lists at any time with
all open issues
all closed issues
all issues to one label
all issues assigned to a person
all issues of a milestone
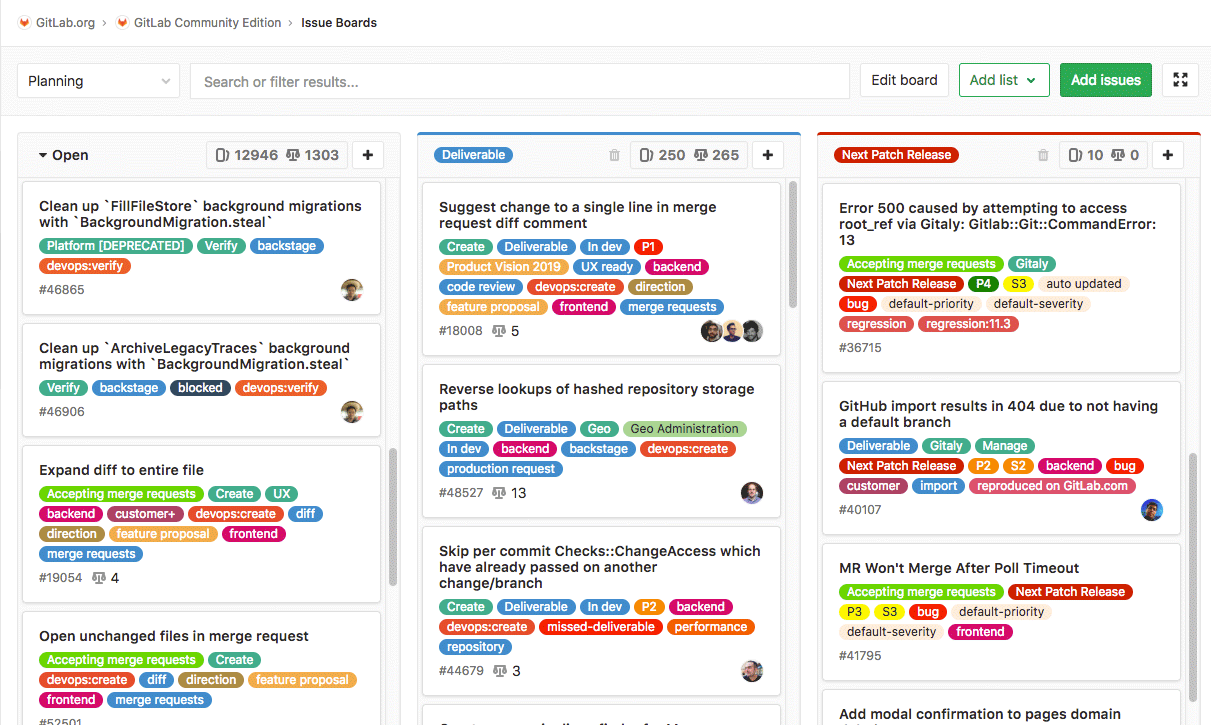
Kanban board¶
Collaboration¶
GitLab not only offers you version control of the source code, but also improves the cooperation between the developers:
they can review, comment on and improve changes
they can share the source code with others, improve reuse and inner sourcing.
they can work in their own copy of the repository
Continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) accelerate testing and deployment
Analysis¶
GitLab shows who worked on a project and how much
The branches and merges are also shown in the course of time, which also shows how effective the Git workflow is
For each branch of a repository, GitLab shows the proportion of programming and markup languages used
GitLab badges give you a quick overview of different areas of a project, from pipeline status to test coverage to contact options.
2. Code¶
Repositories¶
In each project you can create one or more Git repositories and manage your
files there. In a repository you can also add the configuration file
.gitlab-ci.yml for your CI/CD pipeline.
The web interface supports the display and editing of many markup languages, including Markdown, reStructuredText and Jupyter notebooks.
By transferring your changes to the GitLab server you can not only send a short description of the changes but also
refer to an issue
sign a commit
trigger a GitLab CI/CD pipeline
skip pipelines with
[ci skip]in Git commit
Wiki¶
For each GitLab project, a separate wiki can be used as a documentation system with the following features:
Pages can be created in the web interface or locally with Git
Tables of contents can be created with the
[[_TOC _]]tagDisplay the list of all created wiki pages
View the change history of a wiki page
Customize the sidebar using the
_sidebarfile
Wiki page¶
Snippets¶
With GitLab Snippets you can create parts of code and text and share them with others. These are versioned and can also be edited locally with Git. You can also comment on them.
Snippet¶
3. Build¶
Package registration¶
With GitLab Packages, companies can use GitLab as a private repository for a variety of popular package managers. Developers can create and publish packages that can be defined as a dependency on downstream projects. In particular, Docker containers for projects and groups can also be registered. With GitLab CI/CD Docker images can be used for test, build and deploy your project.
4. Test¶
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD)¶
GitLab supports developers in merging the source code they have written into a shared repository in order to subsequently build and carry out integration tests. And the transfer to the staging or production environment can also be done automatically with GitLab.
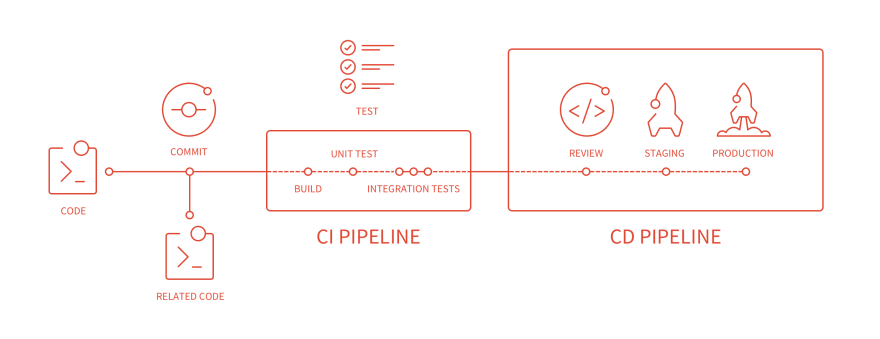
CI/CD pipeline¶
GitLab supports the following features:
- Multi-platform
You can run builds on Unix, Windows, MacOS and any other platform that supports the Go programming language.
- Multilingualism
Build scripts work with Java, Python, C and many other languages.
- Parallel builds
The CI/CD pipeline can be run quickly on several computers at the same time
- Realtime logging
The build log is constantly updated
- Versioned pipelines
The
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile saved in the repository contains the tests to be performed and general production steps- Automatic scaling
GitLab CI/CD can automatically create Docker containers
- Build artifacts
For example, Reports such as PDF, dotenv, etc. are created and made available on the GitLab server. For example, dependencies, licenses, performance and other metrics are also checked automatically.
- Docker support
You can use self-defined Docker containers or create them
- Protected variables
Specific secrets can be saved and used for each environment
Testing¶
A typical use case is that a test fails after a merge request. To carry out further investigations, you can now simply analyse the reports provided.
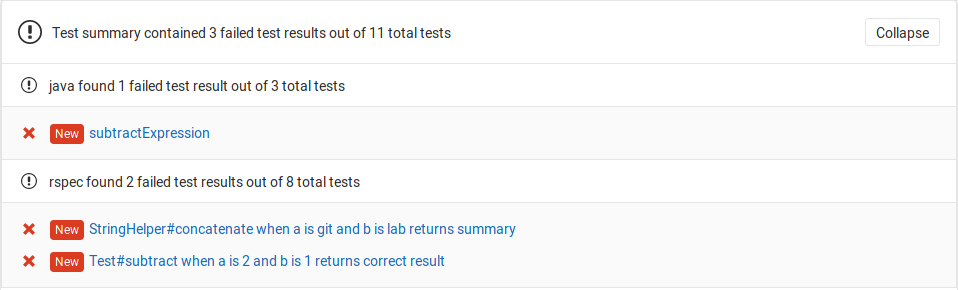
Test report¶
Web Performance Tests¶
GitLab uses Sitespeed.io to measure the
performance of websites and output them in a performance.json file.
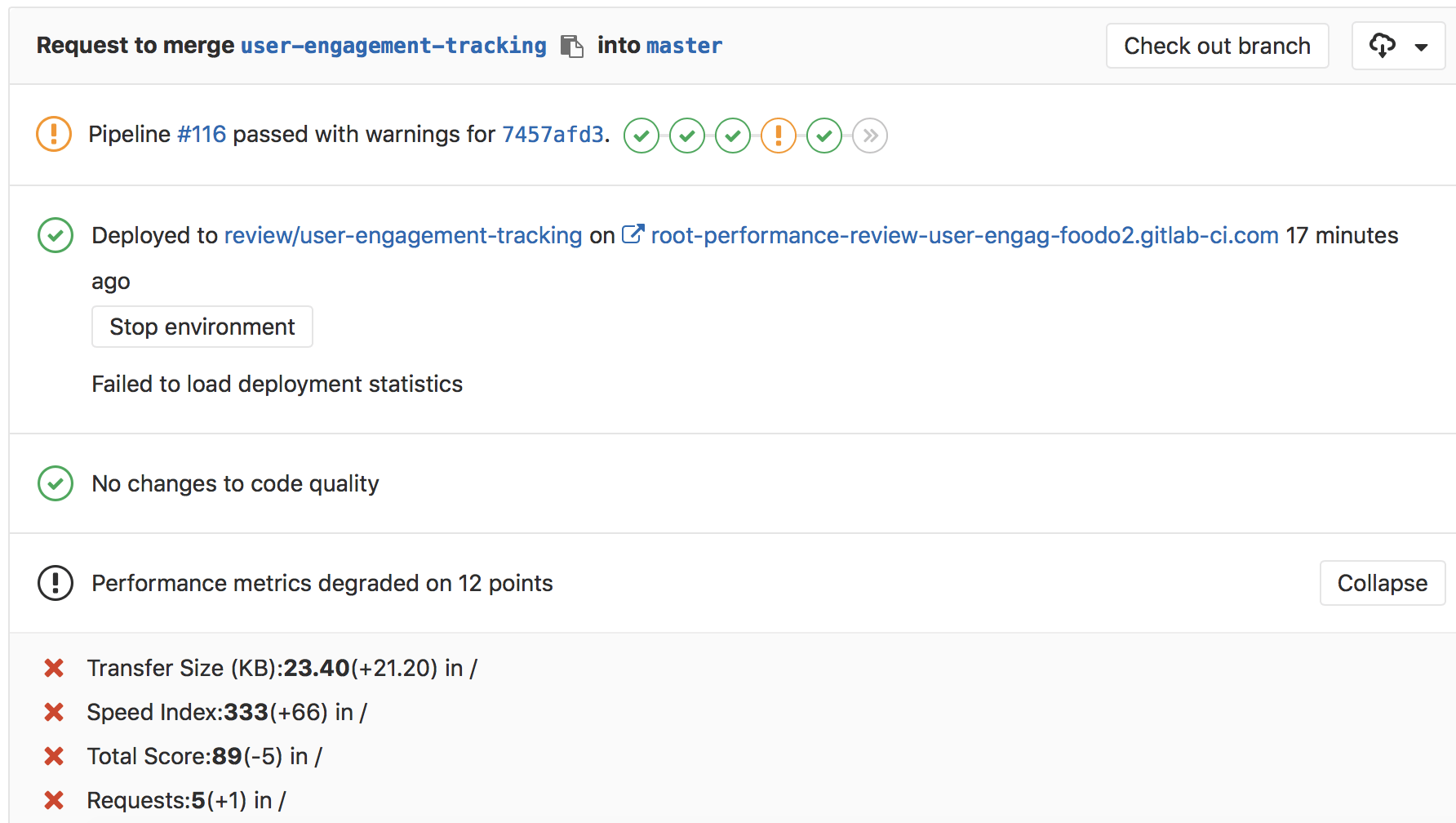
Browser performance test¶
5. Release¶
Typically, a git tag is created before publication to insert a checkpoint in the
version history. In most cases, however, users need compiled objects or other
assets that can be output by the CI system. GitLab uses semantic versioningwith
(Major).(Minor).(Patch) to automatically generate zip, tar.gz, tar.bz2 and
tar files from the tagged source code and the additionally specified assets.
Alternatively, releases can also be created for a specific milestone or a specific date.
Finally, a list of all releases is displayed for each project.
6. Deploy¶
Continuous Delivery (CD)¶
Similar to continuous integration integration tests are automated, continuous delivery automates the roll out on staging and production environments.
Pages¶
To publish a website with GitLab Pages, you can use any static site generator (SSG), e.g. Gatsby, Jekyll, and Hugo to name a few. You can also publish any website that is directly written in simple HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
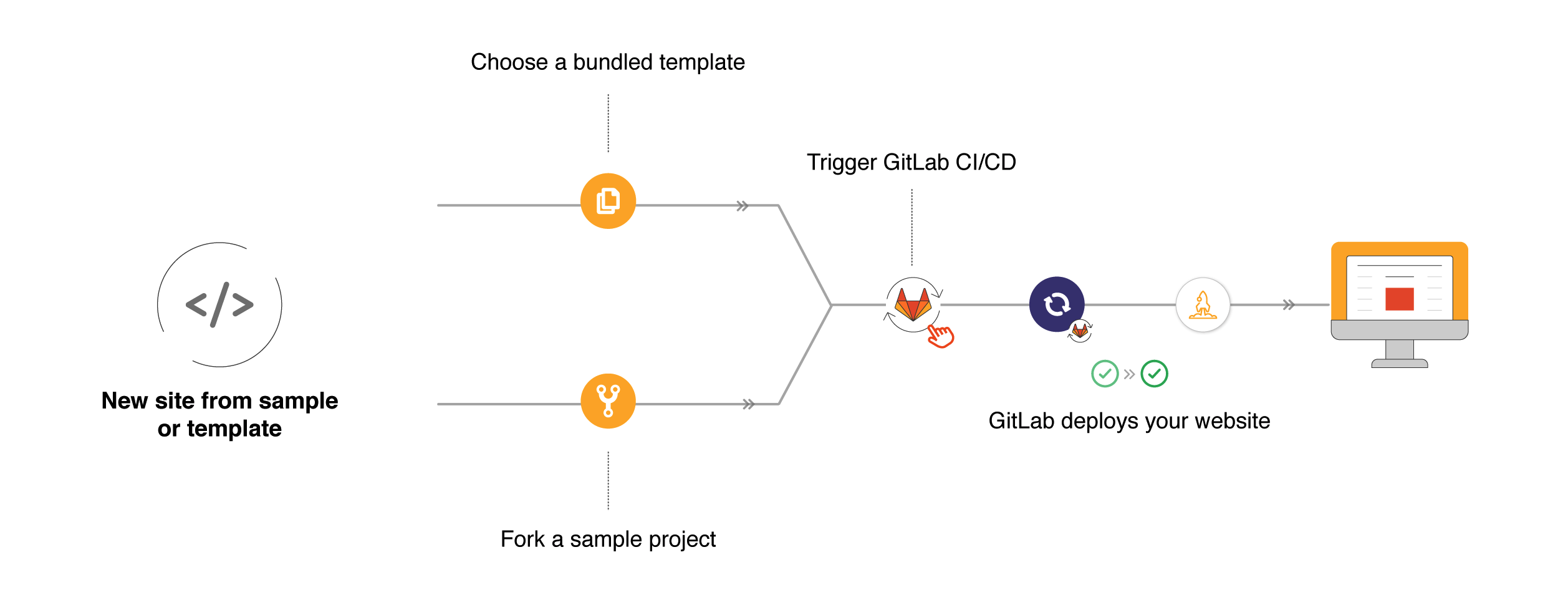
Pages¶
Secrets Management¶
With Vault, confidential information such as environment variables, encryption keys and authentication tokens can be kept safe.
7. Operate¶
Metrics¶
GitLab offers powerful integration with Prometheus to monitor the most important measurement data of your apps directly in GitLab. Metrics for each environment are retrieved from Prometheus and then displayed in GitLab.
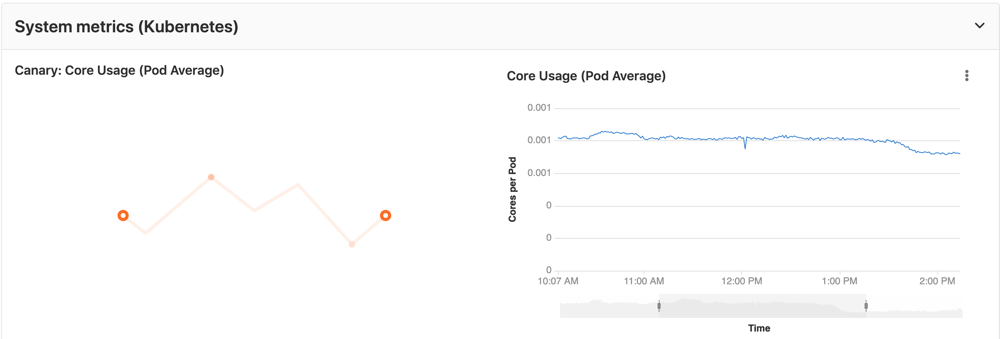
Prometheus dashboard¶
Incident Management¶
You can set up in GitLab that emails are sent in emergencies and related issues are created in GitLab. Specific templates for such issues can be created. GitLab can also automatically close the issues once the problem has been solved.
Status page¶
With the GitLab status page you can create and provide a static website to communicate efficiently with users during an incident. However, only status pages are currently supported in AWS S3. The status page shows you an overview of the last incidents. Clicking on an incident takes you to the details page with
status
title
description
chronologically ordered list of updates
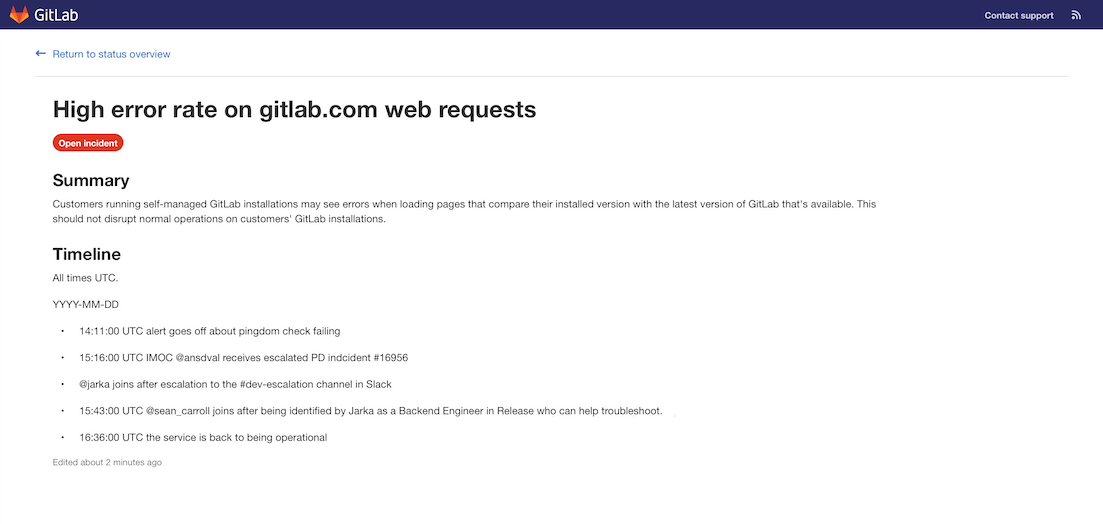
Status page¶
Hosting and data protection¶
Cusy hosts your GitLab DevOps Pipeline according to the German data protection law and taking into account the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This allows you to comply with high IT compliance in the interest of your customers and clients. For more information about how Cusy protects your data, see Security and Privacy.
Customers¶
Many large IT companies use GitLab such as Electronic Arts and Siemens, but also research institutions such as NASA and the University of Washington. GitLab is also used by data center operators like Equinix.
License¶
The Open Source GitLab CE is licensed under the MIT License.
Get in touch¶
I would be pleased to answer your requests and create a suitable offer for the hosting of the GitLab DevOps pipeline.